Burnout: Symptoms, Prevention, and Coping Mechanisms

A term that has been flooding the media over the last few months is ‘burnout’. There has been an increasing amount of concern surrounding it and its causes. This is because of the mounting pressures that have put on our daily activities.
This phenomenon can be understood as the physical and mental health impacts of prolonged stress. It can leave you feeling exhausted and overwhelmed, often related to professional pressures and the feeling of no longer being able to cope in the setting of your job. Burnout should be diagnosed and treated so that it does not cause any related physical issues to worsen.
What is Burnout?
Burnout is a state of complete mental, physical, and emotional exhaustion caused by prolonged stress and overwork. It happens when you push yourself beyond your limits for too long without enough rest or support.
At first, burnout might feel like regular tiredness or stress. You may think you just need a good night’s sleep or a short break. But unlike ordinary fatigue, burnout doesn’t go away with rest. Over time, it drains your energy, motivation, and ability to cope with daily tasks. Even things you once enjoyed may start to feel like a burden.
5 Symptoms That You May Be Experiencing Burnout
1. Experiencing brain fog
One easy way of identifying brain fog is if you notice you have difficulty paying attention or remembering things. You may find that your levels of concentration have been affected. The core reason for this is that high levels of stress cause mental fatigue, which can affect your thought patterns.
2. If you no longer feel the same passion for activities that you used to
If you notice that you are generally feeling quite apathetic or indifferent to their work, passions, or home situation. This can translate into many areas of your life, from food to hobbies or sporting activities that used to bring you joy, but now you have lost interest in them. You will need to take some time for self-reflection to determine if you have genuinely lost interest in those activities or situations or if it may be the result of exhaustion.
3. You start experiencing an increasing amount of negative emotions
Cynicism, frustration, and disillusionment may start to creep in as your mental health is affected. General feelings of pessimism are a strong indication that you are not yourself and may be under too much strain. If you feel overwhelmed with negative emotions, it is probably time to consult a life coach or mental health practitioner in Dubai.
4. Physical symptoms
The most telling sign that you may be experiencing exhaustion is the physical symptoms that come along with it. You may encounter symptoms such as heart palpitations, periods of shortness of breath, headaches, dizziness, and chest pain. Sometimes, it is difficult to analyze whether this is related to burnout or if there may be other health complications that you could be facing. Listen to your intuition and consider the physical symptoms in combination with the emotional and mental symptoms.
5. You are irritable
If you find that it is getting easier and easier for people to get on your nerves or rub you the wrong way, it is a sign of mental fatigue. Usually, the irritability is a result of the other symptoms, especially brain fog and a generally negative mood overall, which will lead to a lack of patience when dealing with others and tasks. If you start to snap at others more frequently or start receiving complaints from those around you about your mood, you should consider taking steps to examine your current mental health situation as well as how to improve it.
The Differences of Burnout, Stress, Depression
It’s easy to confuse burnout, stress, and depression because they share some similar signs. But they are different experiences, and understanding these differences can help you take the right steps to manage them.
|
Condition |
Definition |
Key Characteristics |
|
Stress |
A response to pressure or challenges. |
Feeling overwhelmed but still hopeful. Increased heart rate, muscle tension, anxiety, and frustration. |
|
Burnout |
Long-term exhaustion from prolonged stress. |
Feeling drained, unmotivated, and emotionally detached. Even small tasks feel overwhelming. |
|
Depression |
A serious mental health condition that affects all areas of life. |
Persistent sadness, hopelessness, loss of interest, and low energy. Changes in sleep, appetite, and self-perception. |
What Causes Burnout?
Burnout doesn’t happen overnight. It builds up over time when stress goes unchecked, and the demands placed on you outweigh your ability to recover. While work is a major factor, personal habits and lifestyle choices can also play a role.
Workplace Factors That Contribute to Burnout
-
Excessive workload with no time to recover
-
Feeling pressure to perform beyond capacity
-
Limited say in decision-making and work processes
-
Little to no recognition for effort and achievements
-
Unclear job roles and responsibilities
-
Workplace bullying, micromanagement, or lack of support
Lifestyle and Personal Factors That Increase Burnout Risk
-
Setting impossible standards for yourself
-
Difficulty saying “no” to additional tasks
-
Feeling isolated at work or in personal life
-
Not having an outlet to talk about stress and challenges
-
Working long hours with little time for self-care
-
Struggling to maintain boundaries between work and personal life
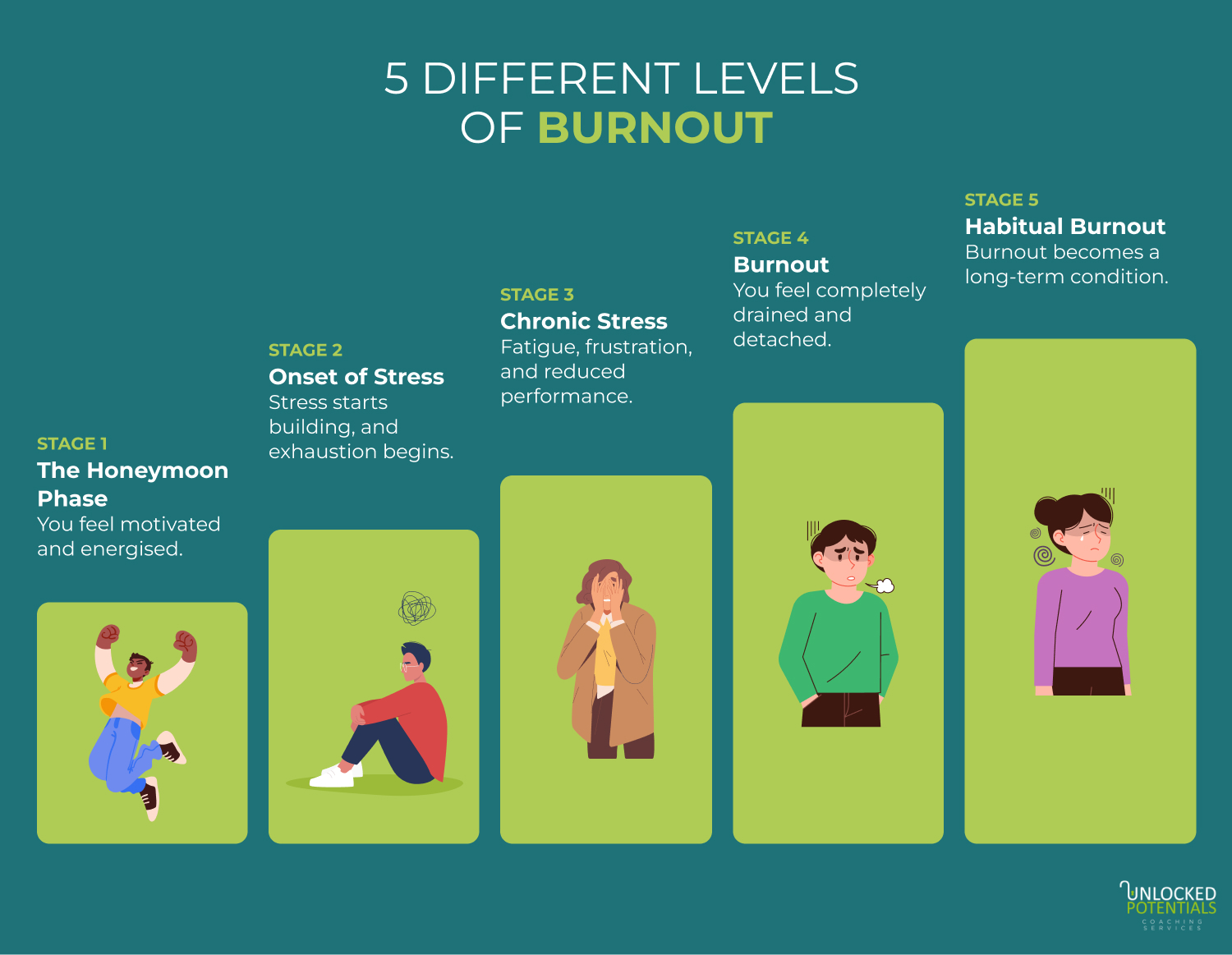
The 5 Progressive Phases of Burnout
Burnout develops over time, moving through different stages until it becomes overwhelming. Recognising these phases early can help you take action before burnout takes a serious toll on your well-being.
Stage 1. The Honeymoon Phase
Burnout often starts on a positive note. You feel excited, motivated, and ready to take on new challenges. Whether it’s a new job, a promotion, or a big project, you’re full of energy and willing to put in extra effort.
At this stage, stress may not feel like a problem because you’re focused on proving yourself and performing well. But if you don’t set healthy boundaries or manage your workload, the constant pressure can start to build without you realising it.
Stage 2. Onset of Stress
As time goes on, stress starts to creep in. You may feel tired more often, struggle to concentrate, or become easily frustrated. Small mistakes or delays might feel more stressful than before.
You may also notice changes in your sleep, appetite, or mood. Work that once felt exciting may start to feel like a burden. At this point, taking breaks and setting limits can help prevent burnout from getting worse.
Stage 3. Chronic Stress
At this stage, stress becomes a constant part of your day. You may feel drained even before your work begins, and simple tasks take longer than usual.
Irritability, frustration, and self-doubt can become more frequent. You might withdraw from colleagues, avoid work, or rely on unhealthy coping habits like overeating or working late just to keep up. If stress is ignored, burnout will continue to develop.
Stage 4. Burnout
Burnout sets in when exhaustion reaches its peak. At this point, you may feel emotionally numb, physically drained, and completely unmotivated. Even time off may not seem to help.
Tasks that used to be easy can feel impossible. You may struggle to care about work, relationships, or even your own well-being. Burnout can also lead to frequent illnesses, headaches, or trouble sleeping. This is when real recovery, not just rest, is needed.
Stage 5. Habitual Burnout
If burnout isn’t addressed, it can become part of your daily life. You may feel stuck in a constant state of fatigue, negativity, or even depression. Work, personal life, and health all suffer, making it harder to break the cycle.
At this stage, recovering from burnout takes more than a break—it requires real changes in how you manage stress, workload, and self-care. Seeking support, setting healthier boundaries, and making lifestyle changes can help you rebuild balance and well-being.
How Can Career Coaches Help Employees Prevent Burnout
Burnout is preventable when the right support and strategies are in place. Career coaches help employees recognise the early signs of burnout, manage stress, and build healthier work habits.
1. Assessing and Identifying Burnout Risks
The first step to preventing burnout is recognising when it’s developing. Career coaches guide employees through self-awareness exercises to help them notice early warning signs, such as constant fatigue, loss of motivation, or emotional detachment from work.
They also help individuals understand the specific stressors contributing to burnout. This could be excessive workload, unclear expectations, or a lack of work-life balance. Identifying these patterns early allows employees to make changes before burnout takes over.
2. Setting Healthy Boundaries and Work-Life Balance
One of the main reasons burnout happens is the inability to set boundaries. Career coaches teach employees how to say “no” without guilt, helping them prioritise tasks and avoid taking on too much.
Time management techniques also play a key role. Learning how to structure the workday, take breaks effectively, and separate work from personal life can reduce stress and improve productivity. Setting these boundaries allows employees to maintain energy and focus without feeling overwhelmed.
3. Developing Coping Strategies for Stress
Stress is unavoidable, but career coaches help employees manage it in a healthier way. Mindfulness, meditation, and relaxation techniques can help reduce anxiety and improve concentration.
Coaches also focus on building emotional resilience. Employees learn how to handle workplace challenges without feeling drained or discouraged. By developing these coping skills, they can respond to stress in a way that protects their mental and physical well-being.
4. Creating a Sustainable Career Path
Burnout often happens when work feels meaningless or misaligned with personal values. Career coaches help employees reflect on their career goals and ensure their work is fulfilling, not just demanding.
They also encourage employees to find purpose beyond job performance. This might include pursuing hobbies, professional development, or meaningful connections at work. A sustainable career is one where employees feel engaged, motivated, and in control of their future.
How to Recover from Burnout and Reignite Your Passion
Burnout doesn’t go away on its own. Recovering from it takes time, effort, and a change in how you approach work and self-care.
Step 1. Recognise and Accept It
The first step in recovering from burnout is acknowledging that it’s happening. Many people try to push through, hoping they will feel better with time. But ignoring burnout only makes it worse.
It’s also important to understand that burnout is not a sign of failure. It happens when you’ve been under too much stress for too long, not because you’re not capable or hardworking enough. Accepting that you need a break and a new approach is the first step towards recovery.
Step 2. Prioritise Self-Care
Recovering from burnout means giving your body and mind the rest they need. Getting enough sleep, eating well, and staying active can help restore your energy levels and improve your overall well-being.
Beyond physical health, self-care also means doing things that bring you joy. Engaging in hobbies, spending time in nature, or simply taking time to relax can help you reconnect with yourself and regain a sense of balance.
Step 3. Seek Support
You don’t have to recover from burnout alone. Talking to a career coach, therapist, or mentor can help you understand why you are burned out and what changes you need to make.
Rebuilding social connections is also important. When you’re burned out, it’s easy to withdraw from others, but spending time with friends, family, or supportive colleagues can give you the encouragement and perspective you need to heal.
Step 4. Make Long-Term Changes
To fully recover from burnout, it’s important to rethink how you approach work and life. This might mean adjusting your workload, setting clearer boundaries, or delegating tasks.
A sustainable work-life balance is key to preventing burnout from returning. Making time for rest, hobbies, and personal growth ensures that work remains a part of life, not something that takes over completely. By taking these steps, you can regain your passion, rebuild your energy, and create a healthier, more fulfilling way of working.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What does burnout feel like?
Burnout feels like constant exhaustion, both physically and mentally. You may struggle to focus, feel detached from your work, and lose motivation even for tasks you once enjoyed.
2. What are the five stages of burnout?
Burnout develops in five stages: The honeymoon phase (high motivation), onset of stress (early signs of fatigue), chronic stress (constant frustration and exhaustion), burnout (complete emotional and physical depletion), and habitual burnout (long-term mental and physical health effects).
3. What does it mean to be burned out?
Being burned out means reaching a point where stress has drained your energy, motivation, and ability to function well. It can make work feel meaningless, affect your health, and impact your personal life.
4. How can you recover from burnout?
Recovering from burnout involves recognising the signs early, prioritising self-care, setting healthy boundaries, and seeking support from a coach, mentor, or therapist. Making long-term changes, like managing workload and improving work-life balance, is key to preventing it from happening again.
5. Can burnout affect physical health?
Yes, burnout can cause physical symptoms like headaches, muscle pain, digestive issues, and a weakened immune system. Long-term burnout can also lead to serious health risks, including heart disease and high blood pressure.
- August 2025
- July 2025
- June 2025
- May 2025
- April 2025
- March 2025
- February 2025
- January 2025
- December 2024
- November 2024
- October 2024
- September 2024
- August 2024
- July 2024
- June 2024
- May 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- August 2023
- July 2023
- June 2023
- May 2023
- April 2023
- March 2023
- February 2023
- January 2023
- December 2022
- November 2022
- October 2022
- September 2022
- August 2022
- July 2022
- June 2022
- May 2022
- April 2022
- March 2022
- February 2022
- January 2022
- December 2021
- November 2021
- October 2021
- September 2021
- August 2021
- July 2021
- June 2021
- May 2021
- April 2021
- March 2020
- February 2020
- January 2020
- December 2019
- November 2019
- October 2019
- September 2019
- August 2019
- July 2019
- June 2019
- May 2019
- April 2019
- March 2019
- February 2019
- January 2019
- December 2018
- November 2018
- October 2018
- September 2018
- August 2018
- July 2015
- May 2014